【Matlab小技巧整理篇】-matlab怎样
2023-04-10 14:42:29
Matlab 编程知识点,温故而知新······
1. 随机数、随机噪声
% 产生 m 个属于 [1, n] 的随机整数
randperm(n, m)
% 产生指定数值(默认 -1 和 1)分布的随机数,可指定元素分布概率
randsrc(10, 10, [-3 -1 1 3; 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.1])
% 产生指定范围的随机数
unifrnd(0, 1:5)
% 产生均值为 0.1 方差为 0.1 的随机数
x = 0.1 + sqrt(0.1)*randn(10000, 1);
% 产生 3 个和为 1 的随机数
r = rand(3, 1);
r = r / sum(r)
% 生成相同的随机数
s = rng;
x = rand(1,5)
rng(s);
y = rand(1,5)
% 每次运行得到相同的结果
% 在使用随机数之前设置
rng(default);
% 添加噪声
y = x + rand(length(x), 1);
y = x + randn(length(x), 1);
2. 字符串分割
% 直接分割
regexp(Numbers = 2500, =, split)
% 分割得到 cell,需要二次处理
textscan(Numbers = 2500, %s %d, Delimiter, =)
3. 数据标准化
y = (x - mean(x)) ./ std(x);
[y, mu, sigma] = zscore(x);
4. R2 计算
x = 1:10;
y1 = x + rand(1, 10);
p = polyfit(x, y1, 1);
y2 = polyval(p, x);
R2 = sumsqr(y2 - mean(y1)) / sumsqr(y1 - mean(y1))
5. 鼠标位置、按键
% 相对 Figure 位置
% Button down function: UIFigure
functionUIFigureButtonDown(app, event)pos = get(app.UIFigure, CurrentPoint)
pos app.UIFigure.CurrentPoint
end
% 相对 Axes 位置
% Button down function: UIAxes
functionUIAxesButtonDown(app, event)pt = app.UIAxes.CurrentPoint;
x = pt(1, 1)
y = pt(1, 2)
end
% 鼠标按键
% normal:左键;alt:右键;extend:中键;open:双击,会触发两次单击
% Button down function: UIFigure
functionUIFigureButtonDown(app, event)button = get(app.UIFigure, SelectionType)
end
6. 剪切板操作
clear; clc;
x = linspace(0, 2*pi, 20);
y = sin(x);
plot(x, y);
% 把 y 值复制到剪切板
clipboard(copy, y);
% 获取剪切板内容
str = clipboard(paste)
% 把当前 figure 复制到剪切板
hgexport(gcf, -clipboard)
7.打开网址
web(https://www.zhihu.com/people/1105936347)
8. 选择颜色
% 单颜色
c = uisetcolor([0.6 0.8 1])
% 色条
cmap = uisetcolormap
9. 符号方程、符号转数值
syms u
f = sym(3);
Eq = sin(f)*u^2 + u + f;
sol = solve(Eq, u)
sol_num = double(sol)
sol_num = vpa(sol)
% 符号替换数字
sol = subs(sol, f, 3)
10. 公式格式化输出到公式编辑器
% 动态脚本输出,直接复制到公式编辑器
syms x
f = taylor(x*exp(x), x, order, 9)
% 复制输出字符串到公式编辑器
latex(f)
11. 文件读写函数汇总
load、save
dlmread、dlmwrite
csvread、csvwrite
importdata
textscan
fprintf
readtable、writetableTaosy.W:【001】文件读写完全版45 赞同 · 6 评论文章

Taosy.W:【039】超好用的文件读写函数readtable和writetable22 赞同 · 10 评论文章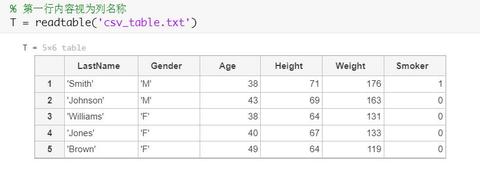

12. 函数可视化
fplot
fimplicit
fimplicit3
fsurf
isosurfaceTaosy.W:【027】函数可视化15 赞同 · 7 评论文章

13. 绘图字体、坐标轴属性设置
clear; clc;
t = 6*pi*(0 : 100) / 100;
y = 1 - exp(- 0.3*t) .* cos(0.7*t);
plot(t, y, r-, LineWidth, 3)
hold on
tt = t(abs(y - 1) > 0.05);
ts = max(tt);
plot(ts, 0.95, bo, MarkerSize, 10)
hold off
axis([-inf, 6*pi, 0.6, inf])
set(gca, Xtick, [2*pi, 4*pi, 6*pi], Ytick, [0.95, 1, 1.05, max(y)])
set(gca, XtickLabel, {2*pi; 4*pi; 6*pi})
set(gca, YtickLabel, {0.95; 1; 1.05; max(y)})
grid on
text(13.5, 1.2, \fontsize{12}{\alpha} = 0.3)
text(13.5, 1.1, \fontsize{12}{\omega} = 0.7)
cell_string{1} = \fontsize{12}\uparrow;
cell_string{2} = \fontsize{16} \fontname{隶书}镇定时间;
cell_string{3} = \fontsize{6} ;
cell_string{4} = [\fontsize{14}\rmt_{s} = num2str(ts)];
text(ts, 0.85, cell_string, Color, b, HorizontalAlignment, Center)
title(\fontsize{14}\it y = 1 - e^{ -\alpha t}cos{\omegat})
xlabel(\fontsize{14} \bft \rightarrow)
ylabel(\fontsize{14} \bfy \rightarrow)
14. 三维曲面属性设置
% 光照
clear; clc;
[X, Y, Z] = sphere(40);
colormap(jet)
subplot(1, 2, 1)
surf(X, Y, Z)
axis equal off
shading interp
light (position, [0 -10 1.5], style, infinite)
lighting phong
material shiny
subplot(1, 2, 2)
surf(X, Y, Z, -Z)
axis equal off
shading flat
light
lighting flat
light(position, [-1, -1, -2], color, y)
light(position, [-1, 0.5, 1], style, local, color, w)
set(gcf, Color, w)
% 镂空
clear; clc;
[X0, Y0, Z0] = sphere(30);
X = 2*X0;
Y = 2*Y0;
Z = 2*Z0;
surf(X0, Y0, Z0);
shading interp
hold on
mesh(X,Y,Z)
colormap(hot)
hold off
hidden off
axis equal
axis off
15. 获取坐标轴范围
limit = axis
xlim = get(gca, xLim)
ylim = get(gca, YLim)
16. 查找绘图对象
% 查找 figure
clear; clc; close all;
x = linspace(0, 2*pi, 20);
y = sin(x);
figure(1)
plot(x, y);
figure(2)
plot(x, y, x, y + 1, --);
figs = findobj(Type, figure)
% 查找线型为 -- 的线
lines = findobj(Type, line, LineStyle, --)
17. 格式化显示
fprintf(%07.4f\n, 2.334)
% 02.3340
fprintf(%07d\n, 2)
% 0000002
num2str(5.5, %07.4f)
% ans = 05.5000
num2str(5.5, %06.4f)
% ans = 5.5000
num2str(2, %06d)
% ans = 000002
18. 刻度显示为 10^4 形式
set(gca, xlim, [0 10e4]);
set(gca, xlim, [0 10e5]);
19. colorbar 设置指数上标
clear;clc;
[x, y, z] = peaks(30);
z = z / 1000;
surf(x, y, z);
cb = colorbar;
cb.Ruler.Exponent = -3;
20. 坐标轴铺满 figure
clear;clc;close all;
x = 0 : 0.1 : 5;
y1 = sin(2*x);
y2 = cos(3*x);
figure
plot(x, y1, o:, LineWidth, 2)
xlabel(x);
ylabel(y);
set(gca, looseInset, [0 0 0 0]);
figure
plot(x, y2, o:, LineWidth, 2)
xlabel(x);
ylabel(y);
set(gca, Position, [0.1 0.1 0.85 0.85]);
21. 设置多种 colormap
clear;clc;
[x, y, z] = peaks(30);
figure;
plot1 = subplot(1,2,1);
surf(x, y, z);
% 获取第一幅图的 colormap,默认为 parula
cMap = colormap;
plot2 = subplot(1,2,2);
surf(x, y, z);
% 下面设置的是第二幅图的颜色,默认是整个 figure 的
colormap(hot);
% 设置第一幅图颜色显示为 parula
set(plot1, Colormap, cMap);
22. 制作 GIF 动图
clear; clc;
x = 0:0.01:1;
n = 1:9;
len = length(n);
im = cell(1, len);
% 单独显示每个图
figure;
for idx = 1:len
subplot(3, 3, idx)
plot(x, x.^idx, LineWidth,3)
title([y = x^, num2str(idx)])
end
% 获取绘制对象
fig = figure;
for idx = 1:len
y = x.^idx;
plot(x, y, LineWidth, 3)
title([y = x^, num2str(n(idx))])
% drawnow
% pause(0.1);
frame = getframe(fig);
im{idx} = frame2im(frame);
end
% 输出文件名
filename = testAnimated.gif;
for idx = 1:len
% 制作gif文件,图像必须是index索引图像
[A, map] = rgb2ind(im{idx}, 256);
if idx == 1
imwrite(A, map, filename, gif, LoopCount, Inf, DelayTime, 0.3);
else
imwrite(A, map, filename, gif, WriteMode, append, DelayTime, 0.3);
end
end
% 读取图像
clear;clc;
% 保存文件名
filename = Model.gif;
% 4张图
for i = 1:4
% 图片路径
fileName = [num2str(i), .jpg];
img = imread(fileName);
% 重定义尺寸
img = imresize(img, [256, 256]);
imshow(img);
% 不显示窗口
set(gcf, visible, off);
% 获取位置
q = get(gca, position);
% 设置左边距离值为零
q(1) = 0;
% 设置右边距离值为零
q(2) = 0;
% 重新设置位置
set(gca, position, q);
frame = getframe(gcf, [0, 0, 200, 200]);
im = frame2im(frame);
imshow(im);
[I, map] = rgb2ind(im, 256);
if i == 1
imwrite(I, map, filename, gif, Loopcount, inf, DelayTime, 0.3);
else
imwrite(I, map, filename, gif, WriteMode, append, DelayTime, 0.3);
end
end
23. 绘制带有误差线的柱状图
clear;clc;close all;
% 获取到颜色
[all_themes, all_colors] = GetColors();
% 生成示例数据
m = 5;
n = 3;
x = 1:m;
y = rand(m, n) + 2;
% 误差限
neg = rand(m, n);
pos = rand(m, n);
% 单系列带有误差线的柱状图
figure;
bar(x, y(:, 1));
hold on
errorbar(x, y(:, 1), neg(:, 1), pos(:, 1), LineStyle, none, Color, k, LineWidth, 2);
hold off
% 多系列带有误差线的柱状图
figure;
% 绘制柱状图
h = bar(x, y);
% 设置每个系列颜色
for i = 1:length(h)
h(1, i).FaceColor = all_colors(i, :);
end
% 单独设置第二个系列第二个柱子颜色
% 这行代码少不了
h(1, 2).FaceColor = flat;
h(1, 2).CData(2,:) = all_colors(6, :);
% 获取误差线 x 值
% 也就是 XEndPoints 的值
xx = zeros(m, n);
for i = 1 : n
xx(:, i) = h(1, i).XEndPoints;
end
% 绘制误差线
hold on
errorbar(xx, y, neg, pos, LineStyle, none, Color, k, LineWidth, 2);
hold off
% 绘制图例
legend({A1, A2, A3});
% 设置 x 轴标签
set(gca, XTickLabel, {label1, label2, label3, label4, label5});
% 试试 barweb
figure;
barweb(y, neg, 1, {label1, label2, label3, label4, label5});
24. OLE 方式写入 Excel
clear;clc;
% 设置文件保存路径
filepath = [pwd, \test.xlsx];
% 检查 Excel 是否已经打开
try
% 若 Excel 服务器已经打开,返回其句柄
excel = actxGetRunningServer(Excel.Application);
catch
% 创建一个Microsoft Excel 服务器
excel = actxserver(Excel.Application);
end
% 设置 excel 属性为可见,0表示不可见
% set(excel, Visible, 1);
excel.Visible = 0;
% 取消保存提示
excel.DisplayAlerts = false;
% 检查文件是否存在
if exist(filepath, file)
workbook = excel.Workbooks.Open(filepath);
% workbook = invoke(excel.Workbooks, Open, filepath);
else
workbook = excel.Workbooks.Add;
% workbook = invoke(excel.Workbooks, Add);
workbook.SaveAs(filepath);
end
% 当前工作表句柄
sheets = excel.ActiveWorkbook.Sheets;
% sheets = workbook.Sheets;
% 返回第1个Sheet句柄
sheet1 = sheets.Item(1);
% 激活第1个表格
sheet1.Activate;
% 修改第1个Sheet的名字
sheet1.Name = test sheet1;
% 页面设置
% 上边距5磅
sheet1.PageSetup.TopMargin = 5;
% 下边距10磅
sheet1.PageSetup.BottomMargin = 10;
% 左边距15磅
sheet1.PageSetup.LeftMargin = 15;
% 右边距20磅
sheet1.PageSetup.RightMargin = 20;
% 设置行高和列宽
% 定义行高向量RowHeight
sheet1.Range(A1:A4).RowHeight = [40, 20, 40, 20];
sheet1.Range(A1:C1).ColumnWidth = [30, 10, 40, 20];
% 合并单元格
sheet1.Range(A1:C1).MergeCells = 1;
sheet1.Range(A3:C3).MergeCells = 1;
% 设置单元格的边框
sheet1.Range(A1:B1).Borders.Weight = 3;
sheet1.Range(A4:C4).Borders.Item(3).Linestyle = 0;
sheet1.Range(A4:C4).Borders.Item(4).Linestyle = 0;
% 设置单元格对齐方式
sheet1.Range(A1:B3).HorizontalAlignment = 3;
sheet1.Range(C1:C3).VerticalAlignment = 1;
% 写入单元格内容
sheet1.Range(A1).Value = 写入内容1;
sheet1.Range(A3).Value = 写入内容2;
% 设置字号
sheet1.Range(A1:B3).Font.size = 11;
sheet1.Range(A1).Font.size = 16;
sheet1.Range(A1).Font.bold = 2;
% 如果当前工作文档中有图形存在,通过循环将图形全部删除
shape = sheet1.Shapes;
% 返回文档中Shape对象的个数
shapeCount = shape.Count;
% while shapeCount > 0
% shape.Item(1).Delete;
% end
if shapeCount ~= 0
for i = 1 : shapeCount
shape.Item(1).Delete;
end
end
% 插入图形
% 生成一个Figure
fig = figure;
% 设置 fig 尺寸且不可见
set(fig, Position, [400, 400, 300, 300], visible, off)
% z = peaks(40); % 这么写图片空白
peaks(40);
% 图形复制
hgexport(fig, -clipboard);
% 图形粘贴
% 选中 sheet1 的 D3 单元格,插入直方图
sheet1.Range(D3).Select;
sheet1.Paste;
% sheet1.PasteSpecial;
% 删除图形句柄
delete(fig);
% 保存文档
workbook.Save;
workbook.Close;
excel.Quit;
25. OLE 方式写入 Word
clear;clc;
% Matlab 操作 Word 文档
% 设置文件保存路径
filepath = [pwd, \test.docx];
% 检查 Word 是否已经打开
try
% 若 Word 服务器已经打开,返回其句柄
word = actxGetRunningServer(Word.Application);
catch
% 创建一个Microsoft Word服务器
word = actxserver(Word.Application);
end
% 设置 word 属性为可见,0表示不可见
% set(word, Visible, 1);
word.Visible = 1;
% 检查文件是否存在
if exist(filepath, file)
document = word.Documents.Open(filepath);
else
document = word.Documents.Add;
document.SaveAs2(filepath);
end
% 句柄获取
content = document.Content;
selection = word.Selection;
paragraphFormat = selection.ParagraphFormat;
% 页面设置
% 上边距60磅
document.PageSetup.TopMargin = 60;
% 下边距45磅
document.PageSetup.BottomMargin = 45;
% 左边距45磅
document.PageSetup.LeftMargin = 45;
% 右边距45磅
document.PageSetup.RightMargin = 45;
% 标题
content.Text = test word;
% 设置文档内容的起始位置
content.Start = 0;
% 设置字号为16
content.Font.Size = 16 ;
% 字体加粗
content.Font.Bold = 4 ;
% 居中对齐
content.Paragraphs.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenter;
% 设置下面内容的起始位置
selection.Start = content.end;
% 回车,另起一段
selection.TypeParagraph;
% 在当前位置输入文字内容
selection.Text = 文字内容1;
% 设置字号为12
selection.Font.Size = 12;
% 字体不加粗
selection.Font.Bold = 0;
% 光标下移(取消选中)
selection.MoveDown;
% 居中对齐
paragraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenter;
selection.TypeParagraph;
selection.TypeParagraph;
selection.Font.Size = 11;
% 在光标所在位置插入一个 4 行 3 列的表格
tables = document.Tables.Add(selection.Range, 4, 3);
% 返回第1个表格的句柄
table = tables;
% table = document.Tables.Item(1);
% 设置表格边框
table.Borders.OutsideLineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle;
table.Borders.OutsideLineWidth = wdLineWidth150pt;
table.Borders.InsideLineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle;
table.Borders.InsideLineWidth = wdLineWidth150pt;
table.Rows.Alignment = wdAlignRowCenter;
table.Rows.Item(2).Borders.Item(1).LineStyle = wdLineStyleNone;
% 设置表格列宽和行高
columnWidth = [50, 50, 200];
rowHeight = [20, 25, 20, 200];
for i = 1 : 3
table.Columns.Item(i).Width = columnWidth(i);
end
% 设置表格的行高
for i = 1 : 4
table.Rows.Item(i).Height = rowHeight(i);
end
% 设置每个单元格的垂直对齐方式
for i = 1 : 4
for j = 1 : 3
table.Cell(i,j).VerticalAlignment = wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
end
end
% 合并单元格
table.Cell(1, 2).Merge(table.Cell(1, 3));
table.Cell(2, 2).Merge(table.Cell(3, 3));
table.Cell(4, 1).Merge(table.Cell(4, 3));
selection.Start = content.end;
selection.TypeParagraph;
selection.Text = 文字内容2;
% 右对齐
paragraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphRight;
selection.MoveDown;
% 写入表格内容
table.Cell(1, 1).Range.Text = 内容1;
table.Cell(3, 1).Range.Text = 内容2;
table.Cell(1, 1).Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft;
table.Cell(3, 1).VerticalAlignment = wdCellAlignVerticalTop;
table.Cell(1, 1).Borders.Item(2).LineStyle = wdLineStyleNone;
table.Cell(1, 1).Borders.Item(4).LineStyle = wdLineStyleNone;
% 如果当前工作文档中有图形存在,通过循环将图形全部删除
shape = document.Shapes;
% 返回文档中Shape对象的个数
shapeCount = shape.Count;
if shapeCount ~= 0
for i = 1 : shapeCount
shape.Item(1).Delete;
end
end
fig = figure;
% 设置 fig 尺寸且不可见
set(fig, Position, [400, 400, 300, 300], visible, off)
% z = peaks(40); % 这么写图片空白
peaks(40);
% 图形复制
hgexport(fig, -clipboard);
% 图形粘贴
% Selection.Range.PasteSpecial;
table.Cell(8,1).Range.Paragraphs.Item(1).Range.Paste;
% 删除图形句柄
delete(fig);
% 设置视图方式为页面
document.ActiveWindow.ActivePane.View.Type = wdPrintView;
% 保存文档
document.Save;
document.Close;
word.Quit;
26. SVD 解病态线性方程组
clear;clc;
% 创建一个典型的病态矩阵:Hilbert矩阵
N = 15;
a = repmat(1:N, N, 1);
A = 1 ./ (a + a - 1);
cd = cond(A);
% 输出条件数
disp(cd);
rng(default);
% 随机生成一组解
x = rand(N,1);
% 生成常数项
y = A*x;
% 左除
x0 = A\y;
y0 = A*x0;
% SVD分解
[u,s,v] = svd(A);
% 方法一:去掉极小奇异值
lemt = 1e-7;
s1 = diag(1 ./ s(s > lemt));
s1(N,N) = 0;
x1 = v*s1*u*y;
y1 = A*x1;
% 方法二:添加正则项
s2 = diag(1./(diag(s)+lemt*ones(N,1)));
x2 = v*s2*u*y;
y2 = A*x2;
% 结果比较:
disp([x, x0, x1, x2]);
disp([y, y0, y1, y2]);
27. 绘制旋转多边形
clear;clc;close all;
m = 3;
n = 41;
d_angle = 2.25;
rotate = 45;
shift = [0, 0];
figure
SpiralPolygon(m, n, d_angle, rotate, shift);
m = 4;
figure
SpiralPolygon(m, n, d_angle, rotate, shift);
figure;
V = SpiralPolygon(m, n, -d_angle, rotate, shift);
hold on
dx = max(V(1, :)) - min(V(1, :));
dy = max(V(2, :)) - min(V(2, :));
shift = [dx, 0];
SpiralPolygon(m, n, d_angle, rotate, shift);
shift = [dx, dy];
SpiralPolygon(m, n, -d_angle, rotate, shift);
shift = [0, dy];
SpiralPolygon(m, n, d_angle, rotate, shift);
hold off
functionV =SpiralPolygon(m, n, d_angle, rotate, shift)th = linspace(0, 360, m + 1) + rotate;
V = [cosd(th); sind(th)];
C = colormap(hsv(n));
scale = sind(150 - abs(d_angle))/sind(30);
R = Rot2(d_angle);
% hold off
for i = 1:n
if i > 1
V = scale * R * V;
end
plot(V(1,:) + shift(1), V(2,:) + shift(2), Color, C(i,:));
hold on
end
set(gcf, Color, w);
axis equal
axis off
end
functionR =Rot2(theta)theta = theta*pi/180;
R = [cos(theta), -sin(theta); sin(theta), cos(theta)];
end
28. 梯度下降法
案例:梯度下降
clear;clc;
%% 一元函数梯度下降法
% 示例:f(x) = min{(x - 1)^2}
% 梯度:g(x) = 2 * (x - 1)
yita = 0.25; % 学习率,一般设置小一点,否则容易在最小值附近震荡或者不收敛
x1 = -5 : 0.1 : 5;
y1 = (x1 - 1).^2;
iteMax = 1000;
xInit = 4;
yInit = (xInit - 1)^2;
err = 1e-6;
figure(Position, [50, 50, 900, 400]);
subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot(x1, y1, b, LineWidth, 2)
xlim([-5, 5])
ylim([-1, 25])
hold on
plot(xInit, yInit, or, MarkerFaceColor, r)
for i = 1 : iteMax
% x = x + yita * grad;
xNew = xInit - yita * 2 * (xInit - 1);
yNew = (xNew - 1)^2;
% 退出条件
if abs(xNew - xInit) < err
break;
else
PlotLineArrow(gca, [xInit, xNew], [yInit, yNew], r, k)
xInit = xNew;
yInit = yNew;
disp([第, num2str(i), 次迭代结果:, num2str(xInit)]);
plot(xNew, yNew, or, MarkerFaceColor, r)
end
end
hold off
title(梯度下降);
%% 多元函数梯度下降法
% 示例:f(x) = min{x1^2 + x2^2}
% 梯度:g(x) = [2 * x1; 2 * x2]
[x, y] = meshgrid(-5:0.5:5, -5:0.5:5);
z = x.^2 + y.^2;
initX = 4;
initY = 3;
initZ = initX^2 + initY^2;
initValue = [initX; initY];
subplot(1, 2, 2)
contourf(x, y, z, 20);
shading interp
hold on
grad = zeros(1, 2);
e = 0.1;
yita = 5; % Adagrad 更快收敛
for i = 1 : iteMax
% 标准的梯度法 x = x + yita * grad;
% newValue = initValue - yita * [2 * initX; 2 * initY];
% Adagrad 法 x = x + yita * inv(G) * grad;
grad = grad + [(2 * initX)^2, (2 * initY)^2];
newValue = initValue - yita * diag(1 ./ sqrt(grad + e)) * [2 * initX; 2 * initY];
% 退出条件
if norm(newValue - initValue) < err
break;
else
newX = newValue(1);
newY = newValue(2);
newZ = newX^2 + newY^2;
% plot([initX, newX], [initY, newY], -ok, MarkerFaceColor, r)
PlotLineArrow(gca, [initX, newX], [initY, newY], r, k)
initValue = newValue;
initX = newX;
initY = newY;
initZ = newZ;
disp([第, num2str(i), 次迭代结果:, num2str(newValue)]);
end
end
hold off
title(梯度下降);
functionPlotLineArrow(obj, x, y, markerColor, lineColor)% 绘制带箭头的曲线
% 绘制散点图
plot(x, y, o, Color, markerColor, MarkerFaceColor, markerColor);
% 获取 Axes 位置
posAxes = get(obj, Position);
posX = posAxes(1);
posY = posAxes(2);
width = posAxes(3);
height = posAxes(4);
% 获取 Axes 范围
limX = get(obj, Xlim);
limY = get(obj, Ylim);
minX = limX(1);
maxX = limX(2);
minY = limY(1);
maxY = limY(2);
% 转换坐标
xNew = posX + (x - minX) / (maxX - minX) * width;
yNew = posY + (y - minY) / (maxY - minY) * height;
% 画箭头
annotation(arrow, xNew, yNew, color, lineColor);
end
29. Adagrad 多元非线性回归模型
clear; clc;
% z = w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4
% z = 900 * exp(-x / 2) + 50 * y + 10
len = 40;
rng(default);
x = randi(len + 1, len, 1) / 5;
y = randi(len + 1, len, 1) / 5;
z = 900 * exp(-x / 2) + 50 * y + 10;
maxi = max(z);
z = z / maxi;
ratio = 0.0;
z = z + ratio * max(z) * rand(len, 1);
X = [x, y];
fun = @(var, X)var(1) * exp(-X(:, 1) / var(2)) + var(3) * X(:, 2) + var(4);
w = lsqcurvefit(fun, [1, 1, 1, 1], X, z);
w([1, 3, 4]) = maxi * w([1, 3, 4]);
disp([lsqcurvefit 计算结果:, num2str(w)]);
% 梯度下降法学习
% obj = 1 / (2 * len) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4 - z) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4 - z)
alpha = 1; % 学习率大收敛快,可能有震荡
iteMax = 10000;
w1 = 1;
w2 = 1;
w3 = 1;
w4 = 1;
initW = [w1; w2; w3; w4];
err = 1e-6;
J = zeros(iteMax, 1);
G = zeros(size(initW));
e = 0.1;
for i = 1 : iteMax
% gradW1 = 1 / len * (exp(-x / w2)) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y - z);
% gradW2 = 1 / len * (w1 * x .* exp(-x / w2) / w2^2) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y - z);
% gradW3 = 1 / len * y * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y - z);
% grad = [gradW1; gradW2; gradW3];
gradW1 = exp(-x / w2);
gradW2 = w1 * x .* exp(-x / w2) / w2^2;
gradW3 = y;
gradW4 = ones(len, 1);
grad = 1 / len * [gradW1, gradW2, gradW3, gradW4] * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4 - z);
% Adagrad 法 x = x + yita * inv(G) * grad;
G = G + grad.^2;
newW = initW - alpha * diag(1 ./ sqrt(G + e)) * grad;
if norm(newW - initW) < err
J(i + 1 : end) = [];
disp([梯度下降法迭代次数:, num2str(i)]);
newW([1, 3, 4]) = maxi * newW([1, 3, 4]);
disp([梯度下降法迭代结果:, num2str(newW)]);
break;
else
initW = newW;
w1 = newW(1);
w2 = newW(2);
w3 = newW(3);
w4 = newW(4);
J(i) = 1 / (2 * len) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4 - z) * (w1 * exp(-x / w2) + w3 * y + w4 - z);
end
end
% 绘图
figure(Position, [50, 50, 900, 400]);
subplot(1, 2, 1)
loglog(J, LineWidth, 2)
legend([alpha = , num2str(alpha)]);
xFit1 = linspace(min(x), max(x), 30);
yFit1 = linspace(min(y), max(y), 30);
[xFit2, yFit2] = meshgrid(xFit1, yFit1);
zFit = w1 * exp(-xFit2 / w2) + w3 * yFit2 + w4;
zFit = maxi * zFit;
z = maxi * z;
subplot(1, 2, 2)
scatter3(x, y, z, r, filled);
hold on
surf(xFit2, yFit2, zFit);
hold off
title(Adagrad 多元非线性回归模型);
30. 积分问题
clear; clc;
format long;
%% 数值积分
% sample 1
fun1 = @(x) sin(x);
result = integral(fun1, 0, pi)
result = 2.000000000000000
% sample 2
fun2 = @(x) sin(x) ./ x;
result = integral(fun2, 0, 1)
result = 0.946083070367183
%% 解析解
syms x t
% sample 3
y1 = sin(x);
f1 = int(y1, x, 0, t)
f1 =
% sample 4
y2 = sin(x) / x;
f2 = int(y2, x, 0, t)
f2 =
f2_val = double(subs(f2, t, 1))
f2_val = 0.946083070367183
f3 = MyIntegral1(fun2, 0, 1, 10000)
f3 = 0.946083070492669
functionresult =MyIntegral1(fun, minX, maxX, intervalCount)% fun: 函数句柄
% minX: 积分下限
% maxX: 积分上限
% intervalCount: 积分区间份数
% 利用积分的定义来求面积
result = 0;
h = (maxX - minX) / intervalCount; % 步长
for i = 1 : intervalCount
result = result + h * fun(minX + (i - 0.5) * h); % 采用简单矩形公式:面积 = 底 × 高
end
end
31. 批量导入文件
clear;clc;
% 获取路径下所有 png 文件信息
all_images = dir(D:\MyPrograms\DataSet\halcon\*.png)
% 图片数量
image_num = size(all_images, 1)
% 遍历图像
for i = 1 : image_num
folder = all_images(i).folder
name = all_images(i).name
fullname = fullfile(folder, name)
end
32. 浮点数判断相等
编程过程中经常遇到判断两个浮点数是否相等的情况,此时如果直接用 a == b 来做判断,会导致意想不到的错误,肉眼可见判断为 true,但是程序给你判断为 false,原因在于浮点数在计算机里存储会有一定的精度误差,可采用简单方法:% 判定为相等
if abs(a - b) < eps
end
33. 科研绘图必备的60套颜色模板
34. 标题、标签、注释换行
% 用 cell 类型
ylabel({Normalized; optical intensity});
以上就是关于《【Matlab小技巧整理篇】-matlab怎样》的全部内容,本文网址:https://www.7ca.cn/baike/15322.shtml,如对您有帮助可以分享给好友,谢谢。
声明
